Universal Caching, lessons learned from NX
DM PUBLICTL;DR
purity + cache = efficient (thus practical) FP
ChatGPT的一个小趣事
SICP之后,不断的又看到一些FP思想在实际工作中的使用。
近来ChatGPT大火,其中transformer结构中的self-attention有明显的recursive结构。
如何高效地推理?
我的第一反应是,给每个token维护一个 dp[][] ,然后去做状态转移。。。
这样的问题是把这个细节暴露地太多在 GPT() 外面。
参考Transformer Inference Arithmetic,实际使用的实现是为QKV准备一个KV cache。
自然结果是等价的,只是写法不同。但是在我看来,这两种写法再次区分了两种范式:declarative_programming。
incremental build/test. and run?
增量编译几乎是所有build工具的标配。包括test结果,常见被cache起来。
但是很少见run也被增量起来(如果是我孤陋寡闻了,请纠正我)。
是没有用吗?我觉的不是的。工程中常见地用DAG结构去组织不同计算节点。 如果头部的节点变化(不管是binary还是输入)自然需要几乎重跑整个computation graph。
但是如果只是修改尾部节点呢:
可以手动指定,从某个节点开始,输入改成之前某次完整graph的结果。 相当于重新为这个节点准备一个graph。
允许incremental run!
这里propose一种实现incremental run的方案。
NX做了什么
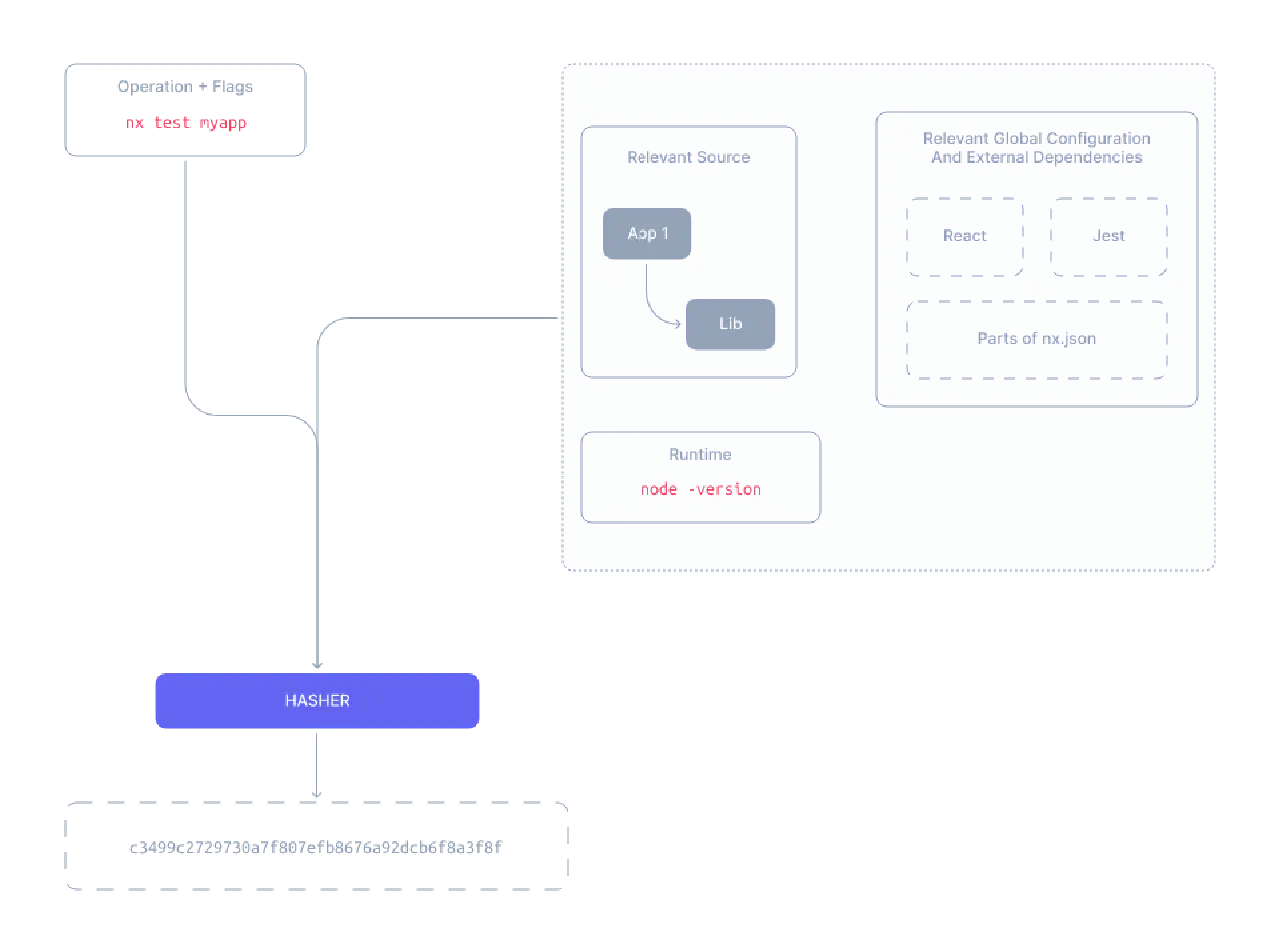
NX提供了一种wrapper,为command或者script,提供KV cache,以支持incremental run。
key如何计算?
NX认为key可以被总结为:
By default, the computation hash for - say - nx test remixapp includes:
- All the source files of remixapp and its dependencies
- Relevant global configuration
- Versions of external dependencies
- Runtime values provisioned by the user such as the version of Node
- CLI Command flags
value如何计算:console print + directories
看看code
始终觉得需要看看代码才直接地理解要怎么做。
wrap command
{ "targets": { "bazel": { "executor": "nx:run-commands", "command": "bazel" } } }run
下面
nx bazel tools就是新的bazel。nx bazel tools build //map/processor/output:mcap_convertor_main结果是:
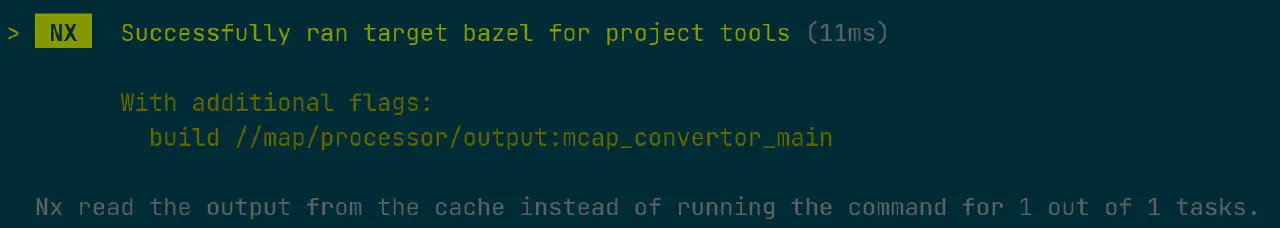
注意到nx这里已经在使用缓存的数据了,不过这里只是指console output。
处理输入输出
首先给我们关心的目录起名字:
{ "namedInputs": { "nas": [ "{projectRoot}/**/*" ], "production": [ "/mnt" ] } }{ "targets": { "bazel": { "executor": "nx:run-commands", "command": "bazel", "inputs": ["default", "production"], "outputs": [ "/tmp/bazel" ] } } }这样,bazel的结果,在input目录修改的时候,就会被invalidate。
如果没有的话,nx会用命中的cache结果,替换
/tmp/bazel目录。输入应该by-content
如果注意到的话,上面的输入目录的hash计算,是基于目录的。
实际使用中,我们希望是基于内容的。比如同样的内容,换了目录,依旧希望可以从cache中拿出结果。
这个可以使用S3中的ETag,ETag只与文件内容有关,与attributes(例如创建时间)无关。 把ETag的结果,放到一个额外的flag或者env里面都可以。
事实上,既然利用了s3的immutability,是不是从cache里拿出来文件也应该更快?这个我还不清楚。
share your cache